Database Backup
We recommend an online database backup is performed daily, ideally when no processes or chains are running as this will simplify restore procedures. Should no suitable window be available, then a backup with the minimal number of running processes and chains will keep additional restoration activities to a minimum.
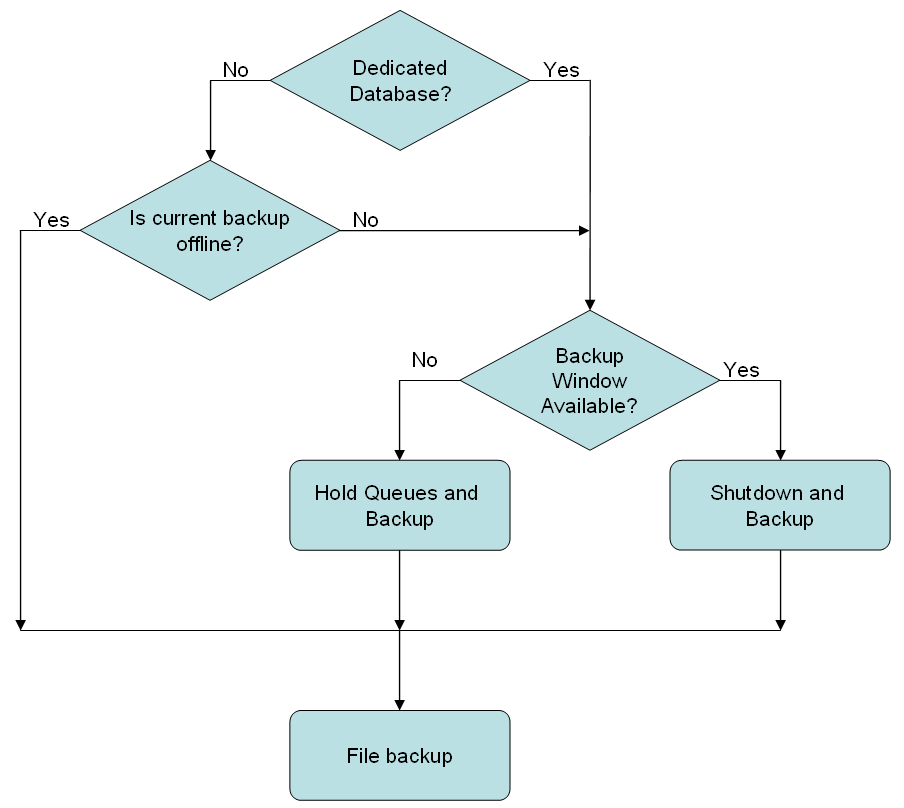
Database backup - Shutdown and Backup
Ensuring that no processes or chains are running simplifies both the backup and restore procedures. The following procedure can be used to ensure that no processes or chains are running:
- Hold all queues.
- Wait for all processes or chains to complete.
- Shut down all process servers (except the System process server).
- Perform the backup.
- Start all process servers.
- Release all queues.
Database backup - Hold Queues and Backup
If it is not possible to perform a backup with no processes or chains running, then holding the queues will prevent new processes and chains from starting, and ensure that the system will not automatically start new processes or chains when it is restored from a backup. The following process can be used:
- Hold all queues.
- Perform the backup.
- Release all queues.
Database backup - Other applications
If other applications (including different instances or older versions of Redwood Server) are present in the database, then it may be desirable to be able to back up only the data for a specific instance of Redwood Server, rather than backing up the entire database, particularly if the other applications store the majority of the data.
Redwood Server stores only tables and indexes in the database, it does not use any proprietary objects (for example public synonyms, views, stored procedures, or triggers). All tables and views have the prefix JCS_. If multiple users or schema have JCS_ tables then you will need to know which database the data are stored in and which username is used to access them.
You need to back up all tables in that database that are owned by the username (or schema for DB2).
Database backup - Multiple instances
If you have multiple instances in the same database, then they need to be installed and accessed as different usernames (schema for DB2). In this situation you can either back up all instances using a database backup, or back them up individually. You will need to ensure that you are working with the correct instance/username during all backup, restore and disaster recovery activities.
If you are using Oracle and have one of the Oracle based versions of Redwood Server some additional considerations apply. You can check if you have such an older version by looking for a public synonym for a package called jcs. If you have one of these older versions, then you cannot install the Redwood Server under the same user (generally SYSJCS).
